Many people wonder what dental caries is and how it affects their oral health. This common problem, often known as tooth decay or cavities, impacts individuals of all ages. Dental caries doesn’t just happen overnight; it involves a slow process that can harm the tooth structure and result in more severe problems if not treated properly.
A surprising fact is that dental caries ranks as one of the most common global diseases affecting humanity today. In this blog post, we will examine the causes of dental caries, identify its symptoms and discuss various strategies for prevention and treatment.
Vetri Dental Care in Tirunelveli aim to equip you with knowledge so you can protect your smile.
Stay tuned for essential tips on avoiding dental caries!
What are the Causes of Dental Caries?
Dental caries, also known as tooth decay, starts when dental plaque collects on the tooth. Plaque is a tacky film composed of bacteria that develops on your teeth. Sugars in the food you eat feed these bacteria, causing them to produce acids.
These acids can break down tooth enamel over time. As the enamel wears away, cavities can form.
Factors like frequent snacking, sipping sugary drinks, and not cleaning your teeth well contribute to plaque build-up and acid production. Tooth decay happens faster if saliva flow is low since saliva helps wash away food and neutralize acid.
Dental fillings might be necessary to treat cavities caused by caries. Regular dental checkups help detect caries early before they lead to cavities due to severe damage, like tooth loss or root caries.
How Does Plaque Contribute to Caries?
Plaque develops on the teeth when bacteria in the mouth mix with sugary foods and drinks. This combination creates a sticky, colorless film that clings to the surface of the teeth. If not eliminated through regular brushing and flossing, plaque can harden into tartar.
Tartar is much harder to clean and provides a perfect environment for bacteria to thrive near the gum line.
Every time you eat or drink something sugary, plaque turns those sugars into acids that attack tooth enamel.
This acid attack weakens the enamel, making it more susceptible to caries development. Over time, this process can lead to small holes in the enamel, known as cavities or dental caries.
Without intervention, these cavities can grow larger and affect deeper layers of the tooth, which may lead to pain, infection, and potentially tooth loss.
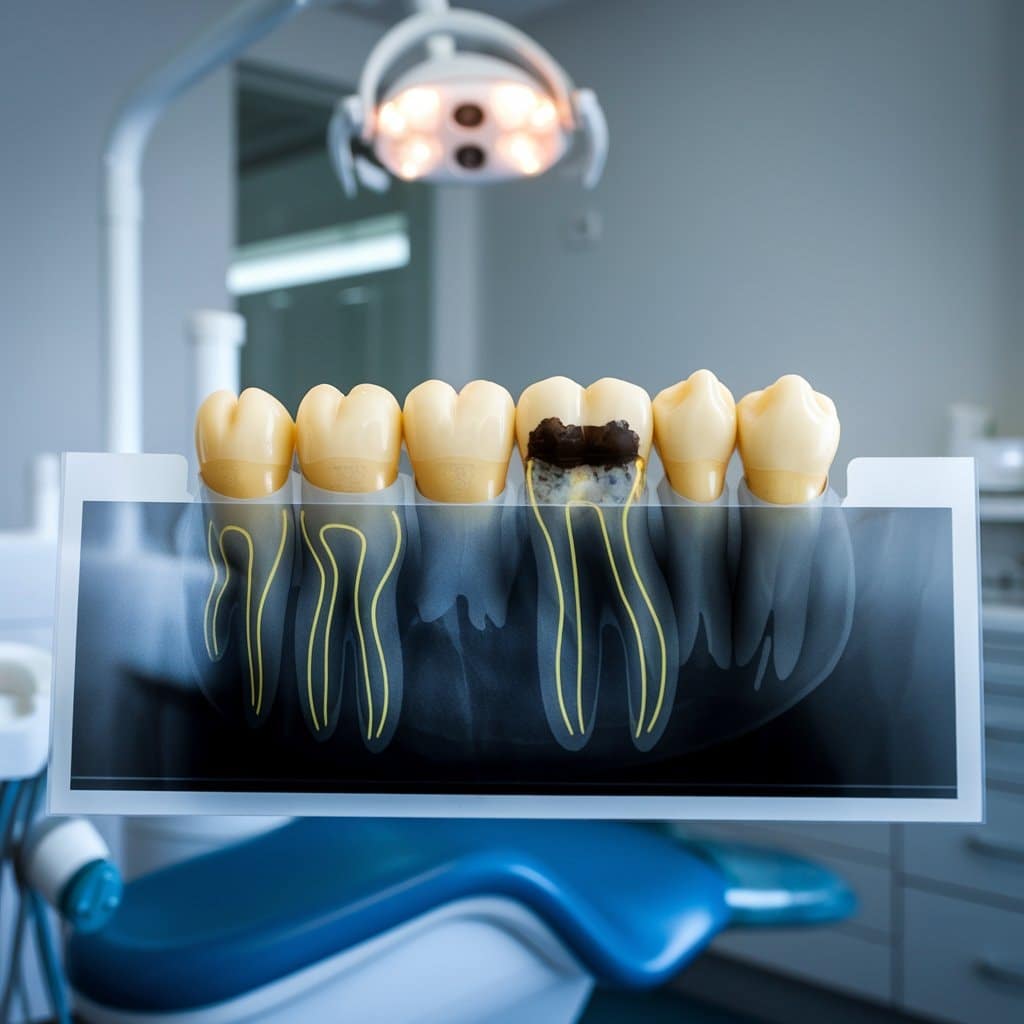
The Role of Tooth Enamel in Caries Development
Transitioning from the discussion of plaque’s contribution to caries, comprehension of tooth enamel‘s part in this matter is essential. Tooth enamel constitutes the firm external layer safeguarding your teeth.
Despite being among the most resilient substances inside your body, it can still be deteriorated by acids created when the bacteria in plaque decompose sugar in your mouth. When this defending blockade is broken, the formation of caries is initiated.
Acids from plaque weaken enamel and additionally lead to minute holes or cavities on the tooth’s surface. Depending on their positioning, these early stages frequently correspond to pit and fissure caries or smooth surface caries.
Hence, the preservation of healthy tooth enamel is crucial in averting dental caries and guaranteeing overall dental health.
Why Tooth Decay Happens: Understanding the Process
Moving from the vital role tooth enamel plays in caries development and tooth decay advances, we now explore why tooth decay occurs. Tooth decay, or dental caries, starts when plaque forms on teeth’ surfaces.
This sticky film contains bacteria that turn sugars from the foods we eat into acids. These acids begin to attack the enamel, leading to the formation of dental cavities. Over time, if not adequately addressed through effective dental care practices, these cavities can penetrate deeper layers of a tooth.
As the damage progresses beyond the enamel into the dentin and potentially affects the pulp inside the tooth, this condition may require more advanced caries treatment options. Factors such as poor dietary choices and inadequate oral hygiene routines significantly contribute to this process.
Regular dental checkups are essential for preventing caries by removing plaque buildup and detecting early signs of decay before they evolve into more severe problems affecting oral health.
What are the Effects of Dental Caries on Oral Health?
Dental caries detrimentally affects oral health in numerous significant manners. The development of caries can substantially harm the tooth’s structure, causing initial cavities and, if unaddressed, progressing to deeper layers such as dentin and pulp.
This chain of events can trigger intense discomfort and infection and, in severe cases, result in total tooth loss. Another particular concern for mature adults is root caries, which attack the rooted part of teeth post-gum recession.
These conditions affect one’s chewing and speaking abilities and also influence overall well-being.
The importance of dental caries prevention lies in preserving healthy teeth and evading intricate dental surgeries.
Disarrangement of remaining teeth due to tooth loss from severe dental caries may demand expensive restoration treatments like bridges or implants. Each phase, from initial decay to tooth loss, deteriorates oral hygiene by offering more surfaces for bacteria colonization, thereby amplifying the threat of further dental ailments.
Implementing efficient prevention methods such as routine dental clinic visits is advisable from an early stage.
How Caries Progression Affects Tooth Structure
Caries progression starts with the softening of tooth enamel, which is the hardest substance in the human body—acid from plaque attacks this protective layer, leading to tiny holes or cavities.
These cavities mark the first stage of dental caries and can affect not just the enamel surface but also the more profound layers of a tooth. As caries advances, it reaches into the dentin, which is much softer than enamel and more sensitive to changes in temperature and acidity.
If untreated, caries can reach the innermost part of the tooth, known as the dental pulp. This area houses nerves and blood vessels. Once infection reaches this area, it may lead to severe pain and ultimately cause a dental abscess.
The progression shows that treating dental caries early on is critical to prevent extensive damage or loss of teeth.
Can Dental Caries Lead to Tooth Loss?
If not treated, dental caries can result in tooth loss. The process begins when bacteria in dental plaque produce acids that attack a tooth’s enamel and dentin. Over time, this action creates cavities and significantly weakens the tooth’s structure.
If such decay progresses without intervention, it reaches the inner pulp of the tooth where nerves and blood vessels reside, causing infection or abscesses. This condition often necessitates endodontic treatment or even removing the affected tooth to prevent further oral health problems.
Neglecting early signs of caries development increases the risk of losing a permanent tooth. Regular dental checkups are vital for recognizing and treating dental caries at an initial stage to avoid extensive damage that could result in tooth extraction.
Implementing effective dental care practices as part of one’s daily routine also plays a crucial role in preventing dental disease progression that leads to tooth loss.
Understanding the Impact of Root Caries
Root caries pose a significant threat to oral health, often leading to more severe problems if left untreated. This form of dental caries affects the root surface of the teeth, which becomes exposed due to gum recession.
Unlike coronal caries, which affect the visible surfaces of the teeth, root caries occur below the gum line. People with a higher prevalence of caries in their medical history or older adults are more susceptible.
Treating root caries quickly is crucial because they can result in tooth loss by harming the part of the tooth that anchors it securely in place. Early diagnosis and care can aid in preventing further damage to permanent teeth and preserve oral health.
Regular dental checkups are essential in identifying such issues before they evolve into severe conditions, ensuring patients maintain a healthy mouth environment.
How is Caries Treatment Administered?
Dentists assess the progression of caries to determine the suitable dental treatment. For very early stages only, fluoride therapy may reverse damage by hardening tooth enamel. This process helps prevent further decay and is crucial for maintaining oral health.
When caries advance, removing the deteriorated portion of the tooth becomes necessary. Dentists then fill these areas with materials like composite resin or amalgam, effectively restoring the tooth’s function and appearance.
For more severe cases where a significant part of the tooth or its pulp is affected, procedures including crowns or root canals are necessary for required. Crowns cap damaged teeth, providing strength and preventing breakage.
Root canal treatment involves:
- Removing infected pulp from inside a tooth.
- Cleaning the cavity.
- Sealing it to block bacteria.
Regular dental checkups are vital to detecting caries early and deciding on an appropriate course of action.
Transitioning into prevention strategies highlights how critical routine care is in avoiding dental complications related to caries.
Exploring Treatment Options for Dental Caries
Exploring treatment options for dental caries begins with understanding the severity of the decay. For early stages, a dentist might simply apply fluoride treatments to help restore the enamel.
This approach can sometimes reverse small cavities by enhancing the teeth’s natural ability to heal. When caries progresses beyond the initial stage, fillings become necessary to remove decay and restore tooth structure.
The material used for fillings varies from composite resins that match the tooth’s color to more durable metals.
In severe cases where caries have damaged a significant portion of a tooth or reached the pulp, more complex procedures are required. Root canal treatment is one option; it involves removing the infected pulp and closing off the area to prevent further damage.
If a tooth is too damaged to be saved, extraction becomes inevitable. Afterward, options like bridges, implants, or dentures help restore function and appearance. Each treatment plan is tailored to individual needs after a comprehensive dental examination to determine the extent and location of caries in oral structures such as interproximal spaces or on occlusal surfaces.
When is a Dental Filling Necessary?
A dental filling becomes necessary when decay has caused a cavity in a tooth. This situation often follows the progression of dental caries, where harmful bacteria break down the tooth’s structure.
Dentists decide to fill a cavity after removing the decayed material to prevent further damage and restore the tooth’s function. Caries risk factors, including frequent snacking on sugary foods, insufficient oral hygiene, and neglecting regular dental checkups, contribute to this need.
Dental professionals use various materials for fillings, such as composite resins that match the color of natural teeth or durable metals for molars subjected to heavy chewing forces.
Identifying caries early means less invasive treatment is required, and more of the tooth can be preserved. After addressing cavities with fillings, maintaining good oral hygiene practices is crucial.
Next, let’s examine what treatments are essential for severe cases of dental caries.
What Dental Treatment is Needed for Severe Cases?
Severe cases of dental caries often require more complex treatments beyond standard fillings. Root canal therapy becomes necessary when the decay reaches the inner pulp of the tooth.
This procedure involves extracting the damaged pulp, sanitizing the inside of the tooth, and sealing it to prevent additional infection. In instances where a tooth cannot be saved, extraction may be the only option.
Following tooth removal, dentists usually recommend replacements such as implants or bridges to restore function and appearance.
For extensive damage across multiple teeth, full or partial dentures might be advised. These solutions help in regaining chewing ability and improving speech affected by missing teeth.
Advanced cases with significant structural loss may benefit from crowns that cover and protect what remains of natural teeth. Each treatment aims at halting further deterioration while restoring oral health and functionality efficiently.
How Can Caries Prevention Be Achieved?
Regular dental checkups are essential for preventing caries. During these visits, dentists can spot early signs of tooth decay treatment and apply treatments like fluoride therapy to strengthen teeth against cavities.
They also provide professional cleanings that remove plaque buildup, a primary contributor to caries development. Informing patients about the significance of these checkups is vital for maintaining oral health.
Healthy eating habits can notably lower the risk of developing dental caries—foods high in sugar and starch fuel plaque formation, leading to dental decay. A diet teeming with fruits, vegetables, and dairy strengthens enamel and lowers caries rates.
Furthermore, executing effective dental care routines at home, such as brushing two times a day with fluoride toothpaste and flossing regularly, helps keep teeth clean from harmful bacteria.
Dental health isn’t only about treating problems; it’s also about preventing them before they start. Frequent care and attention are your optimal protection against dental caries.
Importance of Regular Dental Checkups
Going for regular dental checkups helps prevent caries and can also prevent tooth decay. During these visits, dentists can spot early signs of oral health problems. They look for interproximal caries, occlusal caries, and other issues associated with dental caries, including tooth sensitivity that may arise from early decay.
Early detection means more accessible treatment.
Dental professionals also provide advice on preventing dental caries. They teach about proper brushing techniques and the right dietary choices. This education is crucial for maintaining oral health and avoiding severe dental procedures later on.
Patients learn how to keep their teeth strong through effective dental care practices, reducing the risk of developing carious teeth.
Dietary Choices for Preventing Dental Caries
Dietary choices are vital in the prevention of dental caries. What you eat can either promote oral health or contribute to tooth decay.
- Minimize sugary foods and drinks: Sugar is a significant factor in dental caries development. Bacteria in your mouth consume sugars and produce acids that attack tooth enamel.
- Eat foods rich in calcium: Calcium strengthens the dental hard tissues by reinforcing tooth enamel. Dairy products like milk and cheese yogurt are outstanding sources.
- Choose crunchy fruits and vegetables: Chewing Apples, carrots, and Celery can naturally help clean your teeth by removing plaque.
- Drink plenty of water: Water helps rinse away food particles and maintain high saliva levels. Saliva is essential for neutralizing acids and repairing early caries damage.
- Avoid snacking between meals: Constant snacking provides a steady food supply for bacteria, increasing the risk of developing caries.
- Reduce acidic beverages: Drinks like soda, citrus fruit juices, and sports drinks can erode tooth enamel over time, leading to caries formation.
- Opt for whole grains: Whole grains contain less sugar than their refined counterparts and have more nutrients that support oral health.
- Use sugar substitutes: Consider sweeteners that bacteria cannot metabolize into harmful acids like xylitol, which is often found in chewing gum.
- Incorporate Vitamin D sources: Vitamin D increases calcium absorption in the body, contributing to stronger teeth and lower risks for dental caries.
Effective Dental Care Practices
Adequate dental care practices are vital for preventing and reducing dental caries, as well as maintaining oral health. These steps help avoid the development of dental caries and associated problems.
- Brush teeth twice a day using fluoride toothpaste. This strengthens tooth enamel and fights off harmful bacteria.
- Floss daily to eliminate plaque from areas that your toothbrush cannot access. This reduces the risk of caries at the gum line.
- Limit sugary snacks and acidic beverages that can lead to tooth decay. Foods high in sugar feed the bacteria that cause caries.
- Drink fluoridated water to bolster tooth strength and prevent decay. Communities with fluoridated water see fewer cases of caries.
- Schedule regular dental checkups every six months. These visits facilitate early detection and treatment of dental caries.
- Apply dental sealants on children’s back teeth as a barrier against cavities. Sealants protect the chewing surfaces from caries.
- Consider antimicrobial mouthwashes if recommended by your dentist to control plaque accumulation.
- Use a mouth guard during sports to safeguard teeth from injury, which can make them more susceptible to caries.
- Quit smoking since tobacco use increases the risk of gum disease, which is associated with an increased incidence of caries.
- Follow a balanced diet that consists of a variety of fruits, vegetables, and dairy items supply essential nutrients for oral health.
- Replace your toothbrush every three months or sooner if bristles are frayed, ensuring effective plaque removal.
These strategies are essential for preventing caries by maintaining healthy oral hygiene habits and making informed lifestyle choices.
What factors increase the risk of dental caries?
Various factors increase the risk of developing dental caries, a common concern in oral health. High sugar consumption stands out as one of the primary culprits of early childhood caries. Foods and beverages high in sugar feed the bacteria in plaque, leading to tooth decay.
Poor oral hygiene practices further elevate this risk since regular brushing and flossing are vital for eliminating plaque buildup and preventing caries.
Age is another significant factor; children and older adults are particularly vulnerable. Kids’ fondness for sweets and inconsistent brushing habits can lead to caries on milk teeth.
Older adults face challenges such as receding gums, which expose tooth root surfaces to potential decay. Moreover, certain medications that reduce saliva flow increase the risk since saliva helps protect against tooth decay by eliminating food particles and neutralizing acids produced by bacteria in the mouth.
Identifying High Caries Risk Groups
People with poor oral hygiene fall into high caries risk groups. Not Brushing or flossing regularly prevents plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, from accumulating on teeth. This condition sets the stage for dental caries to form.
Regular dental checkups can catch these issues early, but without them, individuals are more likely to suffer from tooth decay.
Young children and older adults also face a higher risk of developing dental caries. Kids often consume sugary snacks and drinks that contribute to tooth decay, and they may need to be proficient in proper brushing techniques.
Older adults experience receding gums that expose the roots of teeth to cavities. These age groups necessitate focused preventive care and education on effective dental practices to reduce their risk of developing caries.
How Caries May Develop in Different Age Groups
Caries can affect everyone, from toddlers to the elderly, and how it develops varies with age. In children, caries often begins as soon as their first tooth appears. This is due to habits such as frequent snacking on sugary foods or falling asleep with a bottle of milk or juice.
These practices encourage the growth of bacteria that cause caries in young teeth. As kids grow into teenagers, poor dental care routines and increased consumption of junk food contribute to tooth decay’s further development.
For adults and seniors, caries develops differently. Grown-ups face issues like receding gums which expose the roots of teeth to plaque buildup and decay. Moreover, older adults may have fillings from earlier in life that can break down or develop edges where bacteria thrive, leading to new caries around these old restorations.
Wear and tear over the years also make adult teeth more vulnerable to decay despite good oral hygiene habits. Dental caries occur due to a combination of factors at every stage in life, but knowing these tendencies helps target prevention effectively for each age group.
The Progression of Dental Caries in Children
The progression of dental caries in children often starts with the formation of cavities. These tiny holes are the initial stage of tooth decay and signal that the hard tissues of a child’s teeth are under attack by acids produced from plaque.
In young children, one common form of caries is baby bottle tooth decay, which can occur when sugary liquids are frequently exposed to a child’s teeth. This condition often results from prolonged bottle feeding, especially when children are put to bed with a bottle containing milk or juice.
Over time, if untreated, these cavities can grow deeper into the tooth structure, reaching areas where treatment becomes more complex and potentially painful for young patients.
In many cases, this progression leads to adverse effects on oral and dental health in children. Tooth loss is a significant risk if decay reaches the root of a tooth or if infection sets in, necessitating more invasive treatments such as root canals or extractions.
Regular dental checkups are essential for identifying early signs of caries before they escalate to more severe problems impacting a child’s overall well-being and development.
Conclusion
Dental caries, often called tooth decay, is a prevalent but avoidable condition. Regular dental checkups are critical in warding off the onset of dental caries early tooth decay. These appointments permit the identification of early decay indications before evolving into bigger problems demanding thorough treatment.
Maintaining good oral hygiene at home further diminishes the risk of caries formation. Daily brushing with fluoride toothpaste and flossing aids in detaching plaque, the organic substance causing tooth decay.
Protection against tooth decay depends on consuming a balanced diet low in sugar-filled snacks and beverages. Be aware that every daily decision you make influences your oral well-being.
Implementing effective dental care practices ensures a lasting, bright, and healthy smile. Given the reactive prevention techniques and prompt treatment options, losing a permanent tooth due to untreated caries can be entirely bypassed.


