Many people question whether they are eligible for dental implants with gum disease. This is a common concern for those who have lost teeth but also suffer from periodontal issues. Gum disease affects the mouth’s foundation, so deciding to get implants is more complex.
Many people wonder, can you get dental implants with gum disease? This is a common concern for those who have lost teeth but also suffer from periodontal issues. Gum disease affects the mouth’s foundation, so deciding to get implants is more complex.
One key fact is that healthy gums are crucial for dental implant success. This blog will guide you through understanding how gum health impacts implants and what steps you can take to improve your oral health before and after getting implants.
Prepare to learn how to smile confidently again.
How Does Gum Disease Affect Dental Implants?
Gum disease weakens the foundation necessary for dental implants. It leads to bone loss, making it difficult for the jawbone to support new teeth. If not treated, periodontal disease can result in severe bone loss, complicating or even preventing the placement of dental implants.
Healthy gums are crucial because they protect and support dental implant structures just as they do natural teeth.
Healthy gums form the bedrock for successful dental implants.
Infections like peri-implant mucositis and periodontitis around implants arise when bacteria build up under the gum line near an implant, leading to inflammation and further bone damage if left unchecked.
This condition mirrors what happens with natural teeth when gum disease progresses without proper treatment. Dental professionals emphasize good oral hygiene before and after getting implants to prevent such complications and ensure a healthy environment for new teeth.
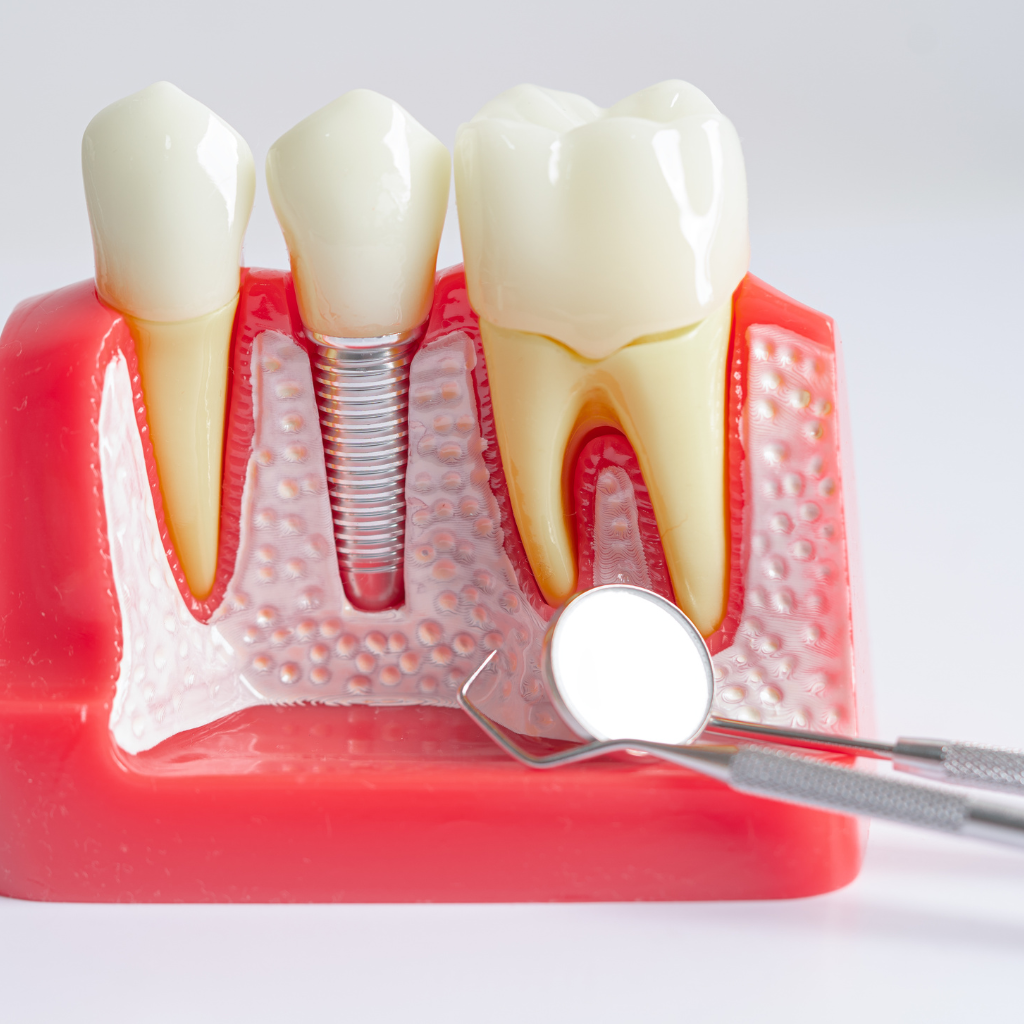
Understanding Gum Disease and Its Stages
Gum disease, or periodontitis, starts as gingivitis with red and bleeding gums. At this early stage, the problem is reversible with good oral hygiene. As it progresses, the gums pull away from the teeth, forming pockets that become infected.
As plaque spreads, the body’s immune system fights off the bacteria below the gum line. Regular dental check-ups can catch these early signs of periodontitis before they lead to more severe gum disease.
If left untreated, advanced periodontitis occurs where fibres and bone supporting your teeth are destroyed. This can cause tooth loss in adults and may require treatments like gum grafts to repair damaged tissue.
Treating gum disease becomes crucial for patients considering dental implants since healthy gums support an implant successfully. Dental professionals focus on controlling infection through deep cleaning methods like scaling and root planing or laser therapy to treat affected areas before proceeding with implant placement.
The Risk of Implant Failure Due to Periodontal Disease
After understanding the stages of gum disease, it’s crucial to consider how this condition impacts dental implant success. Periodontal disease creates an environment that is hostile for implants.
This disease leads to bone loss and inflammation around the gums, both key factors that support a successful implant procedure. Without stable bone density and healthy gum tissue, dental implants may not properly integrate with the jawbone.
Infections like peri-implant mucositis further threaten implant stability by attacking soft tissues. If left unchecked, this can advance to peri-implantitis, affecting both soft and hard tissues.
Such complications often result in implant failure, necessitating removal. Research highlights poor oral hygiene as a leading cause of such failures post-surgery. Therefore, maintaining good oral health practices becomes essential for anyone considering or having undergone dental implant surgery, ensuring their investment lasts for years to come.
How Bone Loss Complicates Implant Placement
Bone loss presents a significant challenge for dental implant placement. For an implant to be successful, it needs the support of healthy bone tissue. If there’s not enough bone, the implant might not stay in place.
This situation often arises from advanced gum disease or when teeth have been missing for a while. The jawbone begins to deteriorate without the stimulation that teeth provide, making implant procedures more complex.
Healthy bones are crucial for dental implants because they anchor the implants firmly in your mouth, explains Dr Suresh Mohan Kumar.
Patients facing such challenges might need additional procedures like bone grafts. This step adds to both the cost and the length of treatment but is necessary to ensure that the dental implants are stable and long-lasting.
Bone grafting involves transplanting bone tissue into areas where it is deficient, creating a solid ground for an implant. This process demands skillful execution by experienced dentists and may affect who can receive dental implants based on their oral health condition and history of gum disease or tooth loss.
Are You a Candidate for Dental Implants with Gum Disease?
Assessing gum health before implant surgery is crucial in determining if dental implants can be obtained with gum disease. Dentists search for indications of healthy gums that are capable of supporting an implant, even among those who have formerly experienced periodontal problems.
They partner with patients to address gum disease prior to initiating the implant treatment process. This implies that if severe gum disease is present, you may be temporarily ineligible until your gums are in a healthier condition.
Any individuals curious about whether lost teeth from receding gums or different types of periodontitis could be swapped with implants should know there are possibilities with the correct steps.
Enhanced oral hygiene and specific treatments aimed at managing gum disease should be the priority. The success of a dental implant largely depends on the surrounding bone area being strong and the gums being infection-free.
Dental professionals employ various methods like gum grafts and comprehensive cleaning regimes to ready your mouth for new teeth, guaranteeing a significant decrease in plaque buildup and tartar before implantation.
Evaluating Periodontal Health Before Implant Surgery
Dentists check your gums and bone health before suggesting dental implants. This step ensures that your mouth can support new teeth. Healthy gums are crucial for implant success, as they help prevent infections that might lead to implant failure.
A detailed examination reveals if you have gum disease or need treatment like a bone graft.
Sometimes, severe gum disease disqualifies patients from getting implants right away. In these cases, dentists work on improving oral hygiene and treating the infection first. Next, they consider procedures such as gum grafts to prepare for successful implant placement.
Can Severe Gum Disease Disqualify You?
Severe gum disease can indeed disqualify you from getting dental implants, as healthy gums are crucial for supporting the implant. Advanced periodontitis, a form of severe gum disease, leads to significant bone loss and infection of the gums, which undermines the stability required for an implant.
Healthy tissue and adequate bone density ensure that dental implants remain fixed in place. If you have uncontrolled diabetes or heart disease related to poor oral health, this could further complicate your eligibility for dental implants.
Treatments like gum grafts and intensive cleaning may help restore your gums to a healthier state. This is essential before proceeding with placing a dental implant. To determine if you’re a candidate despite having severe gum disease, dentists evaluate your oral health thoroughly using X-rays and physical examinations.
They look for signs of inflammation reduction and bone recovery after treatment for periodontitis before approving an implant procedure. Maintaining good oral hygiene after receiving treatments significantly increases the chances of successful implant placement despite previous instances of severe gum disease.
The Importance of Healthy Gums in Supporting an Implant
Healthy gums act as a strong foundation for dental implants, just like roots do for natural teeth. They support the implant by securing it in place and protecting against bacteria that can lead to infections.
Without healthy gums, an implant cannot bond properly with the jawbone’s health, which can increase the risk of implant failure. This makes treating gum disease vital before proceeding with any tooth replacement options.
A stable and infection-free gum environment is crucial for the long-term success of dental implants.
Good oral hygiene practices play a significant role in maintaining gum health post-implant placement. Brush twice a day with fluoride toothpaste floss regularly, and use interdental brushes to remove Plaque are key actions everyone should take.
These steps help prevent peri-implant mucositis—a condition that can progress to more serious infections around an implant if left untreated.
What Treatments Are Available for Gum Disease Before Implant Placement?
Treating gum disease before getting dental implants is crucial. Dentists often recommend a deep cleaning to tackle Plaque and tartar buildup can lead to gum disease. Scaling and root planing is a procedure used to address this and remove bacteria from beneath the gums.
For more severe cases, a dentist might suggest gum grafts to repair areas where significant recession has occurred.
Options like bone grafts also prepare patients for successful implant placement by rebuilding lost jawbone. Maintaining good oral hygiene practices plays a key role in preventing future implant failure.
Patients are advised to brush twice daily, floss regularly, and use mouthwash to keep bacteria growth under control.
Options for Gum Graft and Bone Graft
Treating gum disease effectively requires addressing both the soft tissues and the bones that support teeth. Gum grafts and bone grafts are vital treatment options that can prepare patients for dental implant treatment, especially those suffering from gum recession or bone loss.
- Gum Grafts: This procedure involves taking tissue from another part of your mouth and attaching it to the area where the gum has receded. It helps prevent further gum recession, reducing root exposure and improving the aesthetics of your smile.
- Connective Tissue Grafts: A common method for treating exposed roots by taking tissue from under the flap of skin on your palate (roof of your mouth) and stitching it to the area needing treatment.
- Free Gingival Grafts: Similar to connective tissue grafts, but instead of using tissue beneath the surface, a small amount of tissue is taken directly from the roof of the mouth and attached to the needed site. This method is often used for patients with thin gums who need extra tissue to enlarge their gums.
- Pedicle Grafts: In cases where there’s enough gum tissue near the tooth needing repair, a flap (pedicle) is partially cut away and then moved sideways to cover the exposed root.
- Bone Grafting: This is crucial when there’s not enough bone to support dental implants due to bone loss. The procedure involves placing a material where bone is missing, providing a scaffold for new bone to grow on.
- Autograft: Taking bone from another site in your own body and using it in the area needing bone regeneration. Commonly, bone is harvested from other parts of your jaw or chin.
- Allograft: Utilizing human donor bone instead of your bone. This method eliminates the need for a second surgical site on your body.
- Xenograft: Using animal bones (usually bovine) as a framework for your bone to grow over and replace through time.
- Synthetic Options: Bone substitute materials such as hydroxyapatite or calcium phosphates are designed to promote your body’s natural ability to rebuild bone.
- Guided Bone Regeneration (GBR): Accompanies many bone graft procedures by placing a barrier membrane over the graft site to protect it from bacteria and encourage new bone growth.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP): Used alongside grafting procedures, PRP derived from your blood can stimulate healing and promote faster regeneration of both soft and hard tissues.
Each option offers its unique benefits depending on individual needs, such as the extent of gum recession or degree of bone loss surrounding missing teeth. Dental professionals will evaluate these variables carefully before recommending an appropriate course for gum disease-treated areas, prepping them for successful dental implant placement.
Improving Oral Hygiene to Prevent Implant Failure
After considering options for gum graft and bone graft, improving oral hygiene stands as a crucial step to prevent implant failure. Maintaining good oral hygiene is essential for the longevity of dental implants and overall oral health.
- Brush your teeth twice a day using fluoride toothpaste. Fluoride strengthens tooth enamel and fights decay.
- Floss daily to remove Plaque from places your toothbrush can’t reach. This helps prevent gum disease around implants.
- Use an antimicrobial mouthwash to help reduce bacteria in your mouth. It aids in preventing infections.
- Quit smoking as it harms gum health and decreases the success rate of dental implants.
- Limit sugary snacks and drinks since sugar encourages plaque growth, leading to gum disease.
- Attend regular dental check-ups every six months or as recommended by your dentist. These visits allow early detection of problems.
- Discuss with your dentist the best tools for cleaning around implants, like interdental brushes or water flossers.
- Avoid hard foods that can damage your implants or natural teeth, such as ice or candy.
- Drink plenty of water throughout the day to help cleanse your mouth and keep it hydrated.
- Educate yourself on the signs of peri-implant mucositis, such as inflammation or bleeding around the implant, so that you can seek prompt treatment.
Implementing these steps into your daily routine will ensure that both your natural teeth and implants remain in a healthy condition, safeguarding against the development of gum disease and ensuring the durability of dental treatments like implants.
Addressing Plaque and Tartar Build-up Pre-Implant
Cleaning away Plaque and tartar before getting a dental implant is crucial. Dental professionals often stress the importance of good oral hygiene for patients looking to get implants.
Plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, accumulates on teeth daily. If not removed regularly, it hardens into tartar. This hardened deposit can lead to gum disease, risking the success of an implant.
Dentists use special tools to remove tartar and treat gum inflammation caused by plaque build-up. Patients must maintain good oral hygiene at home, too. Brushing twice a day and flossing are key steps in preventing new Plaque from forming.
A clean mouth supports healthy gums, ensuring that dental implants have the strong foundation they need to last.
How to Keep Your Gums Healthy After Getting Dental Implants?
Maintaining healthy gums after getting dental implants is crucial for implant success and overall oral health. Start with a daily dental care routine that includes brushing twice, flossing at least once, and using mouthwash can help prevent the buildup of Plaque around your implants.
This practice helps fight gum disease and keeps your gums strong enough to support the implants.
Make sure to visit your dentist regularly for check-ups. These visits allow dentists to spot any early signs of peri-implant mucositis or other symptoms that could threaten your implants.
Eating a balanced diet rich in vitamins also plays a vital role in keeping your gums healthy. Foods rich in vitamin C and calcium can boost gum health and ensure the longevity of your dental work.
Daily Dental Care Routine for Implant Success
Taking proper care of dental implants is essential for their success and longevity. A solid oral hygiene routine prevents peri-implant mucositis and ensures your new teeth remain healthy.
- Brush your teeth twice a day using a soft-bristled toothbrush. This action removes Plaque and prevents tartar build-up around the dental implant.
- Floss daily to remove food particles and Plaque from between your teeth and around the implant. Special floss designed for implants can help prevent damage to the area.
- Use an antimicrobial mouthwash to fight against bad breath and reduce bacteria in your mouth that could lead to gum disease.
- Avoid smoking, as it can weaken bone structure and negatively affect the healing process of your dental implant.
- Limit sugary foods and drinks, which promote the growth of bacteria leading to gum disease, a leading cause of tooth loss.
- Wear a mouthguard if you grind your teeth at night to protect both natural teeth and implants from undue stress.
- Attend regular dental check-ups every six months or as recommended by your dentist to ensure early detection of any issues with your implants or overall oral health.
Maintaining these steps as part of your daily dental care routine is essential for keeping your gums healthy and ensuring the success of your dental implants. Leading into our next topic, let’s explore how regular dental visits aid in preventing gum disease.
Regular Dental Check-ups to Prevent Gum Disease
After setting a daily dental hygiene routine for successful implant care, the subsequent essential step is frequent dental appointments to avoid gum disease. Dental professionals are crucial in identifying early indications of periodontitis that may go unnoticed at home.
These expert assessments can identify concerns such as tough tartar accumulation and concealed Plaque, which poses a risk to your gums and implants. Consistent check-ups enable dentists to conduct deep cleanings necessary for preserving healthy gums around a dental implant.
Being proactive is more effective than reactive, particularly in relation to gum health.
Dental professionals are also able to provide customized guidance on enhancing oral hygiene routines based on your unique circumstances. They propose adjustments to your brushing method or suggest particular toothbrushes or flossing instruments that aid in defending against gum disease.
Staying consistent with these visits ensures any potential issues are dealt with promptly, keeping your gums and implants in optimal condition.
Understanding the Role of Diet in Gum Health
Eating the right foods plays a critical role in keeping your gums healthy. Foods rich in vitamin C and calcium, for example, can strengthen the bone surrounding your teeth and help prevent gum disease.
Crunchy fruits and vegetables can increase saliva production, which cleanses the mouth and removes food particles. This way, a balanced diet supports gum health by reducing the risk of developing periodontal diseases.
On the other hand, sugary snacks and acidic beverages contribute to plaque buildup. Plaque hardens into tartar if not removed, leading to gingivitis – an early form of gum disease.
Limiting these harmful foods while maintaining good oral hygiene practices enhances your chances for successful dental implants despite having had gum issues before. Healthy lifestyle choices thus directly impact both natural teeth and implant success rates.
Can Gum Disease Be Prevented to Ensure Implant Longevity?
Preserving gum health is essential to extend the life of dental implants. Routine dental appointments are very effective in preventing periodontitis. These regular assessments enable dentists to identify and treat early stages of gum disease quickly.
Ideal practices involve keeping up with oral cleanliness by brushing and flossing daily, which eliminates Plaque that can cause gum disease.
Identifying initial symptoms such as gums bleeding or bad breath can facilitate immediate treatment, hence preventing further harm. Patients should heed their dentist’s counsel on enhancing homecare routines for oral health.
This preventative perspective helps in averting gum disease and also raises the success likelihood of dental implants, thereby prolonging their lifespan.
Effective Strategies to Prevent Gum Disease
Preventing gum disease is crucial to maintaining both oral and overall health. Implementing a few key strategies can greatly reduce your risk of developing this condition, helping to ensure the longevity of your dental implants by taking proper care of them.
- Brush your teeth twice daily with fluoride toothpaste. Helps remove Plaque, which can cause gum disease.
- Floss at least once a day to remove food particles and Plaque from between the teeth and under the gum line.
- Use an antiseptic mouthwash daily to kill bacteria that might cause gum disease.
- Quit smoking. Smokers are at a higher risk of developing gum disease compared to non-smokers.
- Eat a healthy diet rich in vitamins and minerals, particularly vitamin C and calcium, which support gum health.
- Limit sugary snacks and drinks since sugar encourages the growth of plaque-causing bacteria.
- Schedule regular dental check-ups every six months or as recommended by your dentist for professional cleanings and to monitor your oral health.
- Ask your dentist about sealants or other preventive measures if you’re particularly prone to cavities or gum disease.
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water, which helps remove food particles and bacteria from the mouth.
- If you notice any signs of gum disease, such as bleeding gums, loose teeth, or persistent bad breath (peri-implant mucositis), consult your dentist immediately for a treatment plan.
Following these steps diligently will significantly help in preventing gum disease, ensuring that both your natural teeth and any dental implants remain healthy for years to come.
Recognizing Early Signs of Periodontitis
As we focus on strategies to prevent gum disease, it’s crucial to know how to spot the early signs of periodontitis. This condition can lead to needing treatments before getting dental implants.
Periodontitis starts with red, swollen gums that bleed easily when you brush or floss. You might also notice bad breath or an unpleasant taste in your mouth that doesn’t go away, signaling the development of gum disease.
Periodontitis often leads to gums pulling away from the teeth, forming pockets that become infected. If untreated, this can cause bone loss, complicating implant placement and may result in losing a tooth.
Early detection allows for effective intervention, preventing more severe complications and preserving healthy gums needed for successful dental implants. Recognizing these symptoms promptly could save your teeth and ensure the longevity of future dental work, such as fixed teeth replacements through implants if you have gum issues.
How Regular Dental Visits Aid in Disease Prevention
After recognizing the early signs of periodontitis, it’s crucial to understand how regular dental visits can prevent such diseases. Dentists play a vital role in not just treating but also preventing oral health issues before they escalate.
By scheduling regular check-ups, patients allow dentists to identify any signs of gum disease early on. These professionals use their expertise to suggest treatments or changes in oral hygiene routines that can halt the progression of periodontitis.
During these visits, dentists also perform professional cleanings, which remove Plaque and tartar build-up that daily brushing and flossing might miss. This preventive measure is key in keeping gums healthy and avoiding complications that could impact dental implants and overall oral health.
Regular dental appointments thus become a cornerstone for maintaining optimal gum health and ensuring the longevity of dental implants.
Conclusion
Regular dental appointments are vital in preventing gum disease and securing the success of dental implants. Keeping healthy gums is essential for both implant durability and overall mouth health.
Gum disease treatments exist to control gum disease, enabling numerous patients to receive a dental implant even if they have had gum problems previously. By adhering to appropriate care plans, which involve daily dental hygiene routines and scheduled visits to your dentist, you can experience the advantages of new teeth while maintaining your gum health.
Acting on gum disease before it advances makes sure that your path of replacing missing teeth with implants is triumphant and enduring.


